This roll-forming machine guide presents a thorough examination of roll-forming technology. It covers its evolution, components (including the machine base, roll stands, and tooling), drive systems, operation procedures, and safety considerations. Starting from defining roll-forming machines, this guide offers valuable knowledge for beginners. It delves into different drive systems and essential setup steps for efficiently operating a roll-forming machine. Moreover, it highlights safety practices and training requirements to guarantee a safe and productive roll-forming operation. This beginner-friendly guide is essential reading for those aiming to gain a fundamental understanding of roll-forming machines and their applications.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Roll Forming Machines
- Components of a Roll Forming Machine
- Operation of a Roll Forming Machine
- Applications of Roll Forming Machines
INTRODUCTION OF ROLL FORMING MACHINES
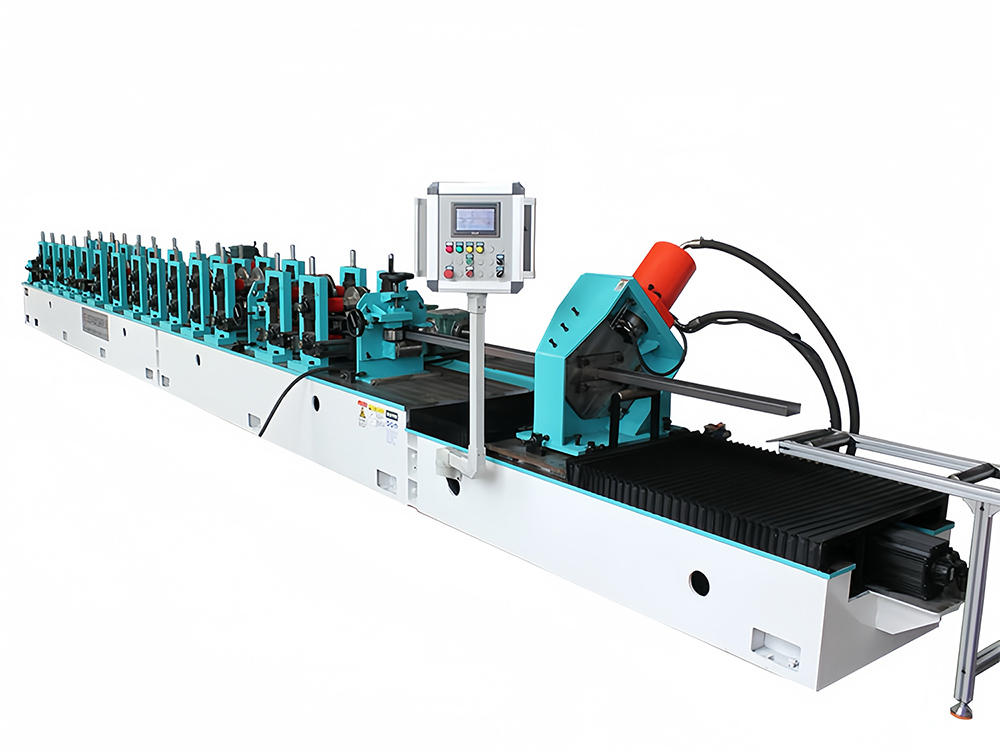
What Is a Roll Forming Machine?
Roll-forming machines are metal-forming equipment that produces continuous lengths of metal with uniform cross-sectional shapes from flat strips or coils. The material is fed through roll stands, each shaping it incrementally until the desired shape is reached. Then, the formed parts are cut to length and stacked for packaging.
The basic principle of roll forming involves multiple roll stands with rollers. These rollers, with specific contours, gradually transform the flat material into the target profile. As the material passes through the rollers, plastic deformation occurs, permanently changing its shape. This process is highly precise and can create complex shapes within tight tolerances.
Overview of the Roll Forming Process and Its Applications
The roll-forming process starts with feeding the metal strip into the machine’s entry guide. It then passes through rollers that bend and shape it. The rollers’ specific contours achieve the required profile. Roll-forming machines are highly versatile, producing various shapes like channels, angles, and tubes.
These machines are used in automotive, construction, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing. They often make components such as metal roofing panels, window frames, door frames, and structural sections. The efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness of roll forming make it ideal for mass – producing high – quality, complex metal profiles.
Understanding roll forming machines helps manufacturers optimize production, reduce waste, and meet modern metal fabrication requirements.
COMPONENTS OF A ROLL FORMING MACHINE
1)Understanding the Roll Forming Machine Base
The base of a sheet metal roll forming machine is the foundation that upholds the entire structure and components. Usually made of high – quality materials like steel or cast iron, it ensures durability and stability during forming. Its design features are vital for the machine’s smooth and accurate operation.
The stability of the base is crucial for maintaining roll and tooling alignment throughout the process. Any deviation or vibration in the base can harm the quality and precision of the formed profiles. Thus, manufacturers focus on base construction, material choice, and design for optimal performance and longevity.
2)Exploring Roll Stands and Tooling
Roll stands are key components in roll forming machines, shaping the metal strip into the desired profile. They have sets of rollers that gradually bend and form the metal as it passes through. The number and arrangement of roll stands vary with the profile’s complexity.
Tooling in these machines includes dies, spacers, and guides used to shape the metal strip as it moves through the roll stands. Different tooling types are used to achieve specific profile shapes, angles, and dimensions. Tooling selection significantly affects the final product’s accuracy, consistency, and surface finish. Manufacturers often customize it based on production requirements.
3)Drive Systems in Roll Forming Machines
Drive systems power and control the metal strip’s movement in roll-forming machines. Common types include mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-drive systems.
4)Mechanical Drive Systems:
These use gears, chains, or belts to transfer power from the motor to the roll stands. They’re reliable and cost – effective for many applications but may have speed and precision limitations.
5)Hydraulic Drive Systems:
These use fluid power for the roll forming process. They’re powerful and flexible, suitable for heavy – duty applications requiring precise control of forming forces.
6)Servo Drive Systems:
These use electronic motors for precise, programmable control. They’re fast, accurate, and repeatable, ideal for complex profiles and quick changeovers.
Understanding these components helps manufacturers optimize production, enhance product quality, and boost efficiency in metal forming.
OPERATION A ROLL FORMING MACHINE
1)Setting Up a Roll Forming Machine
For production setup of a roll forming machine, several crucial steps are needed to ensure it functions well and produces quality profiles. This usually involves preparing tooling, adjusting roll stands, and calibrating the machine according to the profile’s specific requirements.
Proper alignment and calibration during setup are vital as they affect the dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and overall quality of the profiles. Operators must align roll stands, guides, and tooling carefully to ensure the smooth and consistent passage of the metal strip. Also, calibrating the machine’s speed, material – feeding, and cutting mechanisms is key to achieving the desired production parameters.
2)Running a Roll Forming Machine
To operate a roll forming machine, one must understand how to control its speed, material – feeding, and other essential parameters for the desired output. Operators monitor the forming process, make necessary adjustments, and ensure continuous material flow.
Speed control is crucial as it impacts forming quality, production rate, and energy efficiency. Proper material – feeding is also important for consistent results and to avoid jams or misfeeds. Operators must be vigilant during the process, promptly addressing issues like material slippage, tooling wear, or profile irregularities.
3)Safety Considerations in Roll Forming Operations
Safety is of utmost importance in roll forming. Operators must follow essential practices and precautions to reduce accident and injury risks. This includes wearing proper PPE, following safe operating procedures, and being aware of potential hazards near the machine.
Operators should receive comprehensive training on safe operation, including identifying and handling common safety risks, emergency procedures, and proper material and tool handling. Regular maintenance and inspection of safety features like guards, emergency stops, and interlocks are also essential for a safe and efficient environment.
By focusing on setup, operation, and safety, operators can optimize roll forming machine performance and ensure a secure, productive workplace.
APPLICATIONS OF A ROLL FORMING MACHINE
Roll forming machines are versatile industrial equipment that shapes metal sheets into desired cross-sectional profiles. They are widely used in various industries thanks to their efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some of their applications:
Construction Industry: Roll-forming machines are vital in construction, producing metal components for buildings and infrastructure, such as roofing panels, wall cladding, purlins, studs, and other structural elements.
Automotive Industry: In this sector, they create complex and high strength-to-weight ratio automotive parts, like roof rails, door beams, bumpers, and chassis reinforcements.
Storage and Shelving Solutions: Commonly used to make storage and shelving systems for warehouses, factories, and retail spaces, including shelf supports, racking systems, and storage racks.
Suspended Drop Ceiling Solutions: It is widely used in the field of metal ceilings. Common metal ceilings include Square metal ceiling tile, Light gauge steel joist ceilings, Griliato Ceilings, Metal Hanging Strip Ceiling ( baffle ceiling, linear strip ceiling), integrated ceilings, etc
Furniture Manufacturing: The furniture industry uses them to produce metal components like drawer slides, table frames, chair legs, and wardrobe fittings.
Solar Energy Sector: They are crucial for manufacturing mounting structures and frames for solar panels, which need to be precise, durable, and installation-compatible.
HVAC Industry: Employed to fabricate ductwork, ventilation components, air handling units, and other HVAC system parts, as their custom – profile – creating ability suits this sector.
Transportation Equipment: Used in transportation to produce components like chassis rails, side panels, and structural members for vehicles from trailers to buses.
Agricultural Equipment: Used to make agricultural equipment such as grain bins, silos, fencing, and other farm structures, suitable for large – scale applications due to their ability to produce long, continuous profiles.
These applications show the importance of roll forming machines in modern industrial processes across different sectors. Their flexibility, precision, and efficiency make them essential for manufacturing a wide range of metal products.

